Employee motivation is a crucial aspect of any successful organization. It plays a significant role in driving employee performance, engagement, and overall satisfaction at work. As a leader or manager, understanding what motivates your team members can greatly impact their productivity and contribution to the company’s goals.
Read on the fundamentals of employee motivation and learn more about what truly drives our teams!
What is Employee motivation?
Employee motivation refers to the internal and external factors that stimulate desire and energy in people to be continually interested and committed to a job, role, or subject, or to make an effort to attain a goal. It’s what drives an individual to choose to engage in certain behaviors over others. Motivation is deeply connected to individual needs and goals – whether they be for personal achievement, recognition, job satisfaction, security, or financial reward.
There are various theories of motivation, each exploring different aspects of what compels individuals to act. These include intrinsic motivation, which individuals derive from personal satisfaction or interest in the work itself, and extrinsic motivation, which stems from external factors like financial rewards or recognition. Understanding these different types of motivation is essential for effective team management and leadership.
Importance of Motivation in the Workplace

Motivation plays a crucial role in the workplace as it is one of the key factors that drive employees to perform their best and achieve organizational goals. As a driving force behind your employees’ performance and your company’s success, here’s why you should prioritize fostering motivation:
1) Higher Productivity: Motivated employees tend to be more engaged and committed to their work, resulting in higher levels of productivity. When employees feel motivated, they are willing to go above and beyond what is expected of them, leading to increased efficiency and output.
2) Better Performance: Employees who are motivated have a clear sense of purpose and direction. This drives them to set challenging goals for themselves and strive towards achieving them. As a result, they perform better at their jobs as compared to those who lack motivation.
3) Improved Job Satisfaction: An important aspect of motivation is job satisfaction – how content an employee feels with their job. When employees feel motivated at work, there is a strong correlation with high levels of job satisfaction. A satisfied employee tends to be happier at work, leading to lower turnover rates and higher retention rates for companies.
4) Increased Innovation: Motivated individuals possess a forward-thinking mindset that allows them to think creatively outside the box. They come up with new ideas and solutions that can bring about innovation within the organization.
5) Positive Work Environment: The presence of highly motivated employees creates a positive atmosphere in the workplace where everyone strives towards personal growth as well as organizational success together. This not only boosts morale but also fosters teamwork among colleagues.
6) Customer Satisfaction: Highly motivated employees provide excellent customer service since they take pride in representing their company positively. This leads to increased customer satisfaction, which is crucial for any business’s success.
Ultimately, motivated employees are an invaluable asset to any organization looking to achieve long-term success in today’s competitive business world.
Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs
Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs is a well-known theory in psychology that explains the different levels of human needs and how they motivate behaviour. It consists of five tiers, with each level representing a specific need that must be fulfilled before an individual can move on to higher-level needs. At the base of this hierarchy are physiological needs, such as food, water, shelter, and warmth. These basic physical necessities serve as the foundation for all other needs and are essential for survival. Without fulfilling these fundamental requirements, individuals will have difficulty focusing on anything else.

Once physiological needs are met, people become motivated by safety and security needs. This includes financial stability, job security, health insurance benefits, etc. Employees who feel safe and secure in their jobs are more likely to be motivated to work harder because they do not have to worry about meeting their basic survival needs. After satisfying safety and security needs comes belongingness or social needs – the desire for love, and affectionate relationships with family members or coworkers at the workplace also play important roles here.
Humans are social creatures who seek acceptance from others; thus having positive relationships at work can greatly impact employee motivation. The fourth tier is esteem needs which include self-esteem (feeling confident), respect from others (recognition), and achievement( being recognized/rewarded when goals are accomplished). Employees want recognition for their contributions towards achieving organizational goals which enhances their sense of accomplishment leading them closer towards satisfaction.
Finally, the pinnacle of Maslow’s hierarchy is self-actualization – reaching one’s full potential through personal growth and development. This level focuses on challenging oneself intellectually, making use of creativity & problem-solving skills. By providing opportunities for employees’ professional growth organizations boost employee motivation leading to greater productivity, fostering innovation, and contributing positively to overall company performance.
Simply, Maslow’s Hierarchy emphasizes that employees’ most pressing motivators align closely with psychological factors rather than material incentives. Organizations should first focus on addressing lower levels of needs such as providing a safe and secure work environment, building positive relationships, and recognizing employees’ accomplishments before moving on to higher levels like self-actualization. By understanding and utilizing this theory, organizations can create a more motivated workforce that is committed to achieving individual and organizational goals.
Herzberg’s Two-Factor Theory: Factors that lead to job satisfaction vs dissatisfaction
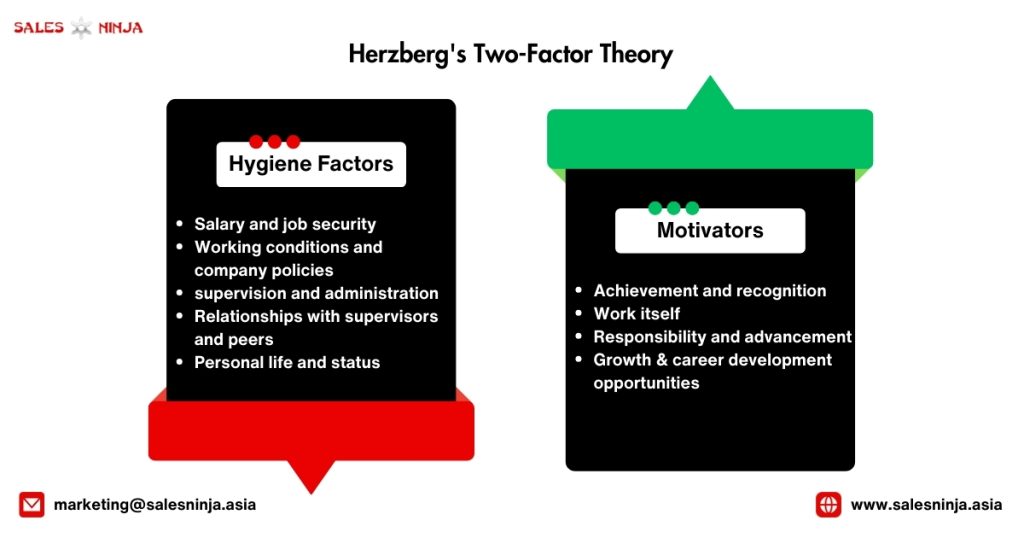
Herzberg’s Two-Factor Theory is a motivation and job satisfaction theory developed by psychologist Frederick Herzberg in the 1950s. This theory suggests that there are two distinct sets of factors that contribute to an individual’s level of job satisfaction or dissatisfaction.
Hygiene Factors: These are factors that, when absent or inadequate, cause dissatisfaction, but their presence does not necessarily motivate employees. They are considered maintenance factors that are necessary to avoid unhappiness but don’t necessarily lead to satisfaction. Hygiene factors include:
- Salary and job security (basic financial security)
- Working conditions and company policies
- Quality of technical supervision and administration
- Relationships with supervisors and peers
- Personal life and status
Motivators: These factors, when present, actively create job satisfaction and are effective in motivating individuals to superior performance and effort. They are related to the nature of the work itself and how the employee feels about the work. Motivators include:
- Achievement and recognition
- Work itself (the degree of challenge or interest the work generates)
- Responsibility and advancement
- Growth and career development opportunities
According to Herzberg’s theory, these two sets of factors operate independently from each other. Hygiene factors primarily influence an employee’s attitude towards their job while motivators have a direct impact on their motivation levels leading them to experience greater fulfillment and enjoyment in their work. Improving hygiene factors may reduce negative feelings within employees related to their jobs; however, fulfilling those needs does not necessarily guarantee job satisfaction.
Similarly motivating employees through incentives alone without addressing any issues related involving poor working conditions or inadequate salaries may only provide temporary boosts in morale rather than sustainable long-term improvement in overall job satisfaction. These findings remain relevant even today where organizations need strategies beyond just monetary benefits when formulating plans designed to improve worker welfare.
Types of Incentives/ Rewards That Drive Employees

As a leader or manager in your organization, understanding the types of incentives that can drive your employees is crucial for fostering a motivated and productive workforce. There are various types of incentives and rewards that you can use to motivate your employees. Let us take a closer look at some of these incentives:
- Monetary Incentives: This is one of the most common forms of employee motivation, where an employee receives financial benefits for meeting or exceeding their performance targets. Examples include bonuses, profit-sharing plans, salary increases, commission-based pay structures, etc.
- Non-monetary Incentives: While monetary incentives can be effective in motivating employees, non-monetary rewards also have a significant impact on employee satisfaction and productivity. These could include flexible work hours, extra vacation days, recognition programs such as “Employee of the Month,” training opportunities, etc.
- Health Benefits: Offering health-related benefits like insurance coverage for medical expenses or gym memberships not only shows that an employer cares about their employees’ well-being but also encourages them to lead healthier lifestyles which can positively affect productivity levels.
- Career Advancement Opportunities: Employees who see potential growth within an organization tend to be more motivated and engaged in their work compared to those with limited opportunities for advancement. Employers can offer promotions based on merit or provide training programs to help develop necessary skills for career progression.
- Employee Stock Ownership Plans (ESOPs): ESOPs are becoming increasingly popular among companies looking to reward long-term commitment from their staff members while also aligning their interests with those of shareholders through company stock ownership.
- Employee Recognition Programs: It is essential to recognize and appreciate employees’ efforts regularly – it helps boost morale and creates a positive work culture leading to increased job satisfaction and retention rates among workers.
- Benefits Linked To Performance Goals: Offering strong motivators such as all-expense-paid vacations or gift cards upon reaching specific performance milestones can drive individuals toward success.
- Team-based Incentives: Encouraging teamwork and collaboration can be achieved by offering incentives for team achievements. This not only promotes a sense of camaraderie but also motivates employees to work together towards a common goal.
- Personalized Rewards: Every employee has different needs and motivations, so it is crucial to offer personalized rewards that cater to their individual preferences. For example, some may value recognition in front of colleagues while others may prefer additional time off or remote working options.
- Employee Stock Purchase Plans (ESPPs): Similar to ESOPs, ESPPs allow employees to purchase company stock at discounted prices, giving them an opportunity for long-term financial growth as well as aligning their interests with the organization’s success.
Remember, the effectiveness of these incentives can vary based on individual employee preferences, job roles, and organizational culture. Regularly seeking feedback and understanding your team’s unique motivations can help tailor these incentives effectively. This balanced approach ensures that your employees are motivated not only by financial gains but also by a sense of belonging, appreciation, and personal fulfilment in their roles.
The Role of Leadership in Employee Motivation
As a leader, you’ve got a big part to play in how motivated your team feels. Your leadership style really shapes their behavior and performance. Remember, it’s up to you to foster an environment where your team members feel engaged, committed, and satisfied with their work.
Make sure to share a vision that really connects with your team. It’s about giving them a clear purpose and a sense of direction in what they do. This way, you’ll see them more satisfied with their jobs and more driven to work together towards your shared goals.
Moreover, acknowledge individual contributions and celebrate collective achievements to boost the morale of your team members. Listen to what your team has to say, give them quick feedback on how they’re doing, and keep them in the loop about what’s happening with the company’s goals and any new changes. Trust me doing this will build a solid trust foundation within your team.

Remember, as a leader, you’re the role model in the office. The way you act – your values, beliefs, and the way you do things – really sets the tone for everyone else. So, make sure what you do mirrors what you expect from your team, especially when it comes to ethics and professionalism.
Your leadership style? It makes a big difference in how motivated your team feels. If you’re calling all the shots, your team might not feel too pumped about their work. They need a bit of freedom to feel invested.
But, if you’re the type to get everyone’s input before making a decision, giving your team a real say in their work, that can be a game-changer. It will make them more satisfied with their job and more committed to the goals you’re all working towards.
So, take a moment and think: Are you the ‘my way or the highway’ type, or do you prefer a team huddle before making your move?
Creating a Work-Life Balanced Environment for Employee Motivation
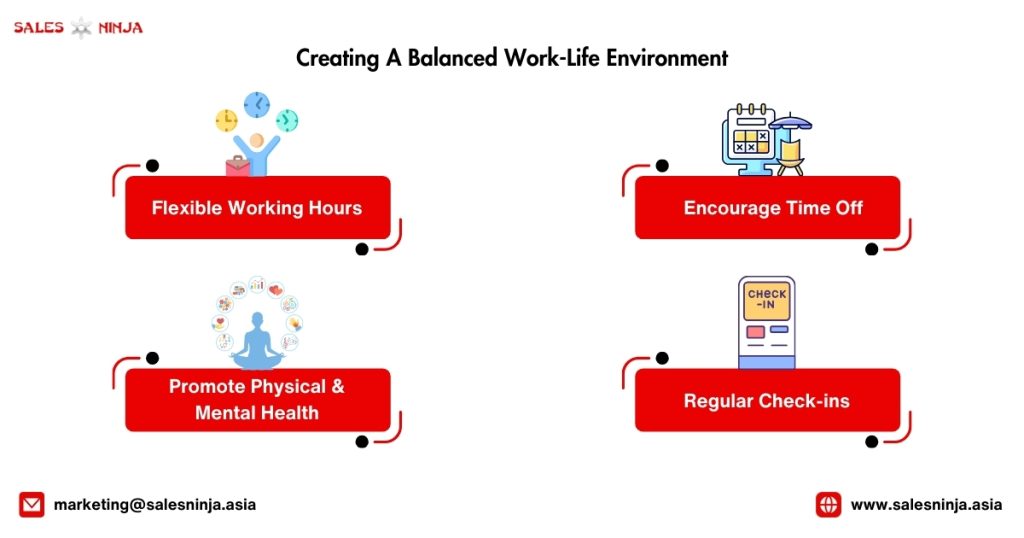
Crafting a workplace that prioritizes work-life balance isn’t just a nice-to-have. It’s a must for keeping your team fired up and ready to go. See, when your employees have the space to balance their work and personal life effectively, it’s like hitting two birds with one stone – they’re happier, and their work gets better.
So, what should be your move?
Flexible Working Hours: Implement flexible working hours or allow remote work options. This enables employees to work during hours they find most productive or balance personal commitments effectively.
Encourage Time Off: Encourage employees to take their vacation time and to fully disconnect from work during their time off. This helps them recharge and return to work with renewed energy and perspective.
Promote Physical and Mental Health: Offer programs or resources that support physical and mental health. Such as gym memberships, wellness programs, or access to counseling services.
Regular Check-ins: Have regular check-ins with employees to discuss their workload. And any challenges they are facing in maintaining a healthy work-life balance.
Motivational Strategies for Different Types Of Employees

Everyone’s different, right? So, adjusting your approach to match the needs and preferences of each employee can truly enhance workplace inclusivity, liveliness, and efficiency. It’s about understanding what drives each individual and leveraging their strengths to not only enhance their job satisfaction but also elevate their performance. Here’s how you can approach this:
Introverts: These employees often prefer quiet, solitary work environments and may feel more energized by spending time alone. They tend to be reflective and thoughtful.
For them-
- Provide a quiet, focused work environment or allow for remote work options where possible.
- Offer tasks that require independent work or deep concentration.
- Recognize their achievements in a more private, one-on-one setting rather than in public forums.
Extroverts: Extroverted employees thrive in social settings and are energized by interactions with others. They are often outgoing, and expressive, and enjoy collaborative work.
For them-
- Encourage participation in team projects or group activities.
- Facilitate opportunities for social interaction within the workplace.
- Offer public recognition of their accomplishments, as they often appreciate social validation.
Proactive Individuals: Proactive employees take initiative and are often forward-thinking. They prefer taking charge of situations and planning ahead.
For them-
- Assign roles that allow them to lead or manage projects.
- Encourage them to set goals and take on challenges.
- Provide opportunities for them to contribute ideas and improvements.
Reactive Individuals: Reactive employees tend to respond to situations as they arise rather than seeking to control them. They are often adaptable and excel in roles that require flexibility and problem-solving.
For them-
- Offer roles that involve problem-solving and adaptability.
- Create a supportive environment where they can respond to changes without pressure.
- Recognize their ability to adapt and handle unexpected situations effectively.
Employee Motivation Statistics You Need To Know
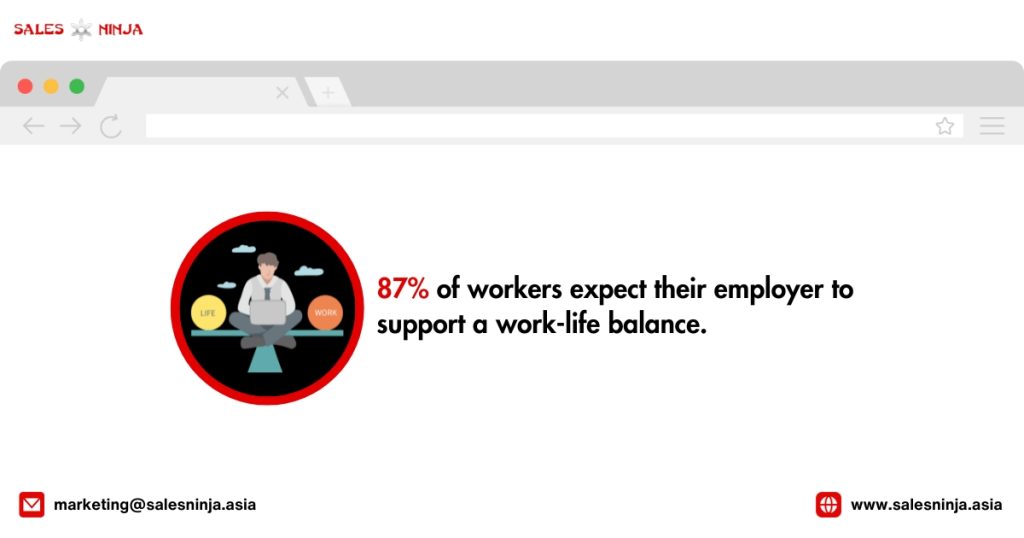
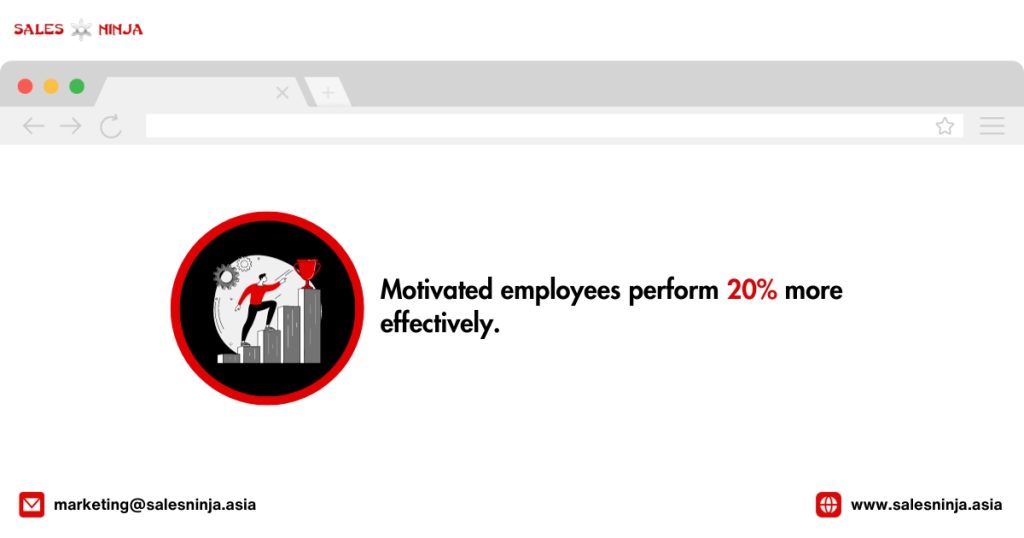
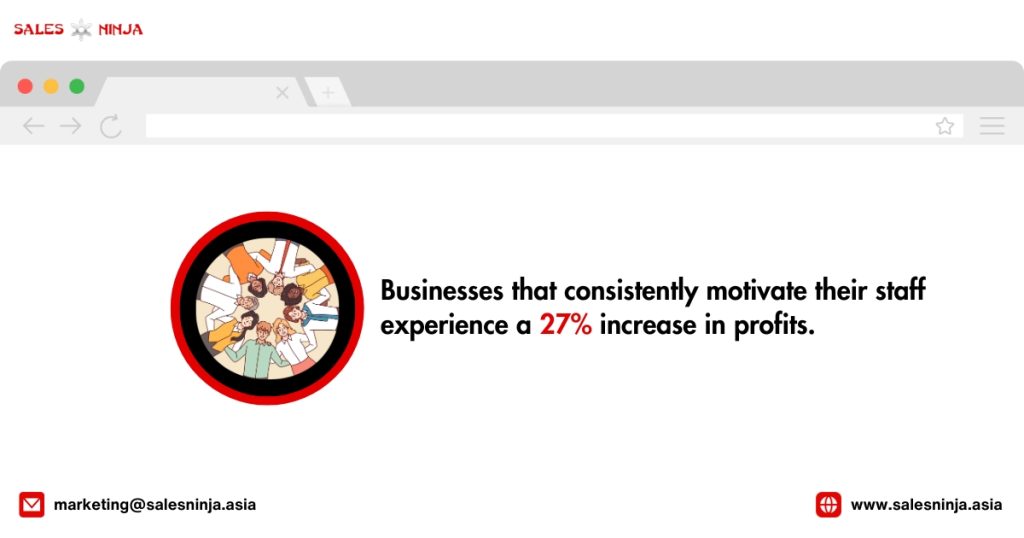
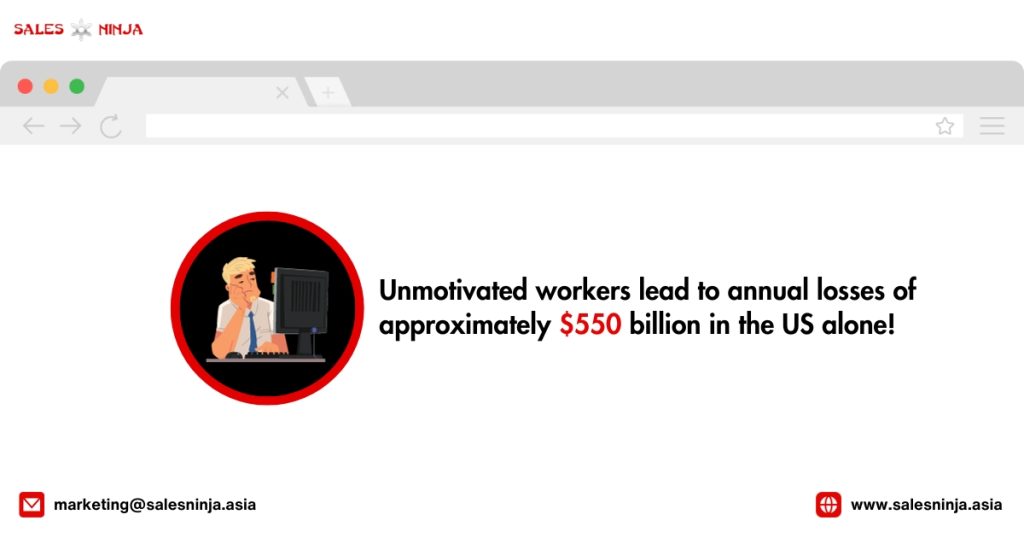
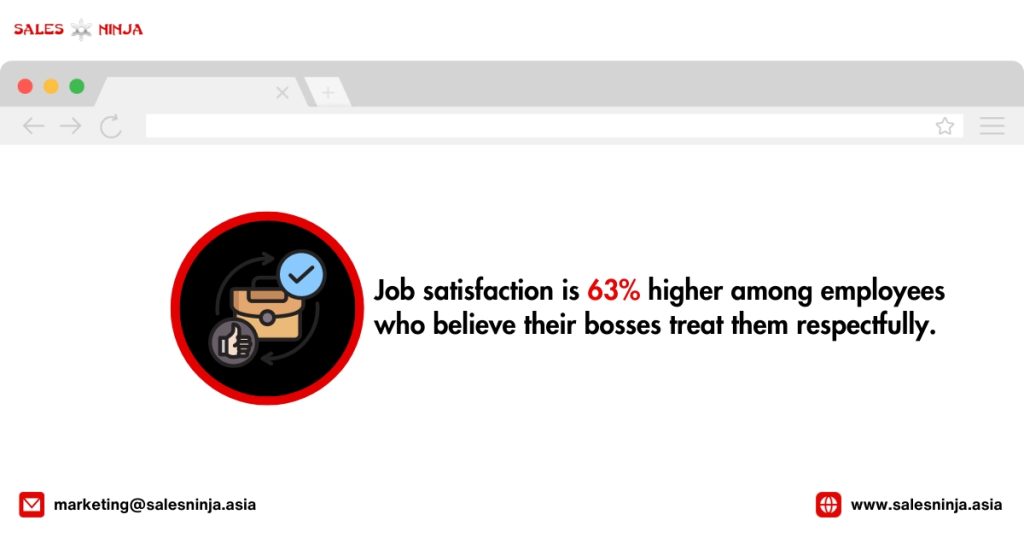
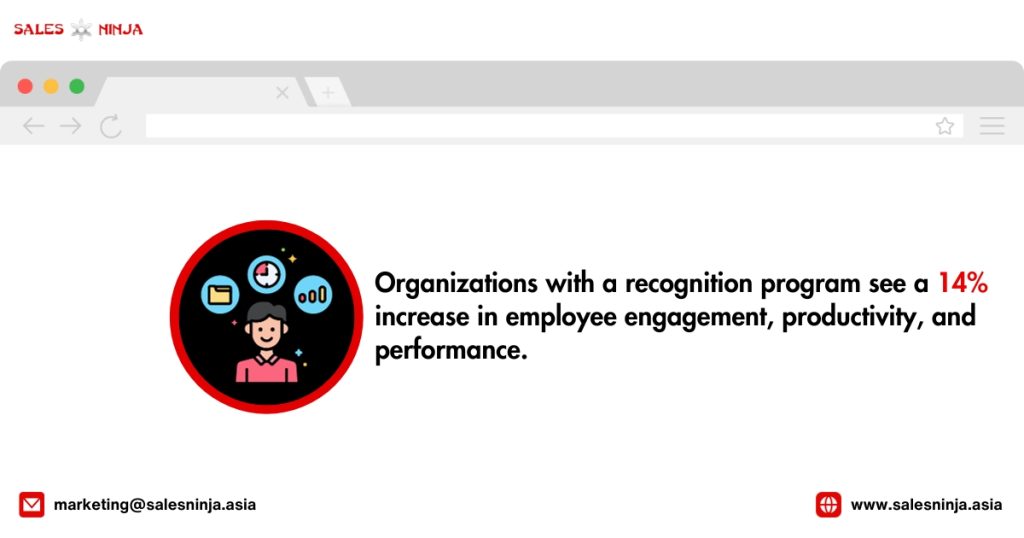
Sources: teamstage.io, plecto.com, smallbizgenius, Deloitte
Boost Your Team’s Motivation with Sales Ninja
In today’s tough market, marked by economic challenges and stiff competition. It’s vital to have a sales team that’s not only skilled but also highly motivated. Sales Ninja’s training program is designed specifically for this environment. We prepare your sales force to deal with global economic shifts, budget cuts, sceptical business owners, and growing competition.
Our program focuses on strengthening your team’s mental resilience and strategic skills. Ensuring they’re ready to outperform in the demanding market. This is an opportunity for your team to transform into sales warriors, ready to tackle challenges and seize opportunities.
We invite you to empower your team with Sales Ninja. Enroll in our program and watch your team’s motivation and performance soar. Contact us to find out more and start your journey to sales excellence.
Get in Touch with Sales Ninja: https://salesninja.asia/contact/




